Esiti
Results of the Re-NetTA project
The Re-NetTA research report is divided into 5 Working Packages (WP) whose extracts are reported below.
The Re-NetTA research project aims to put into practice organizational and operational models and innovative business models related to re-manufacturing and reuse in the context of the transformation of buildings for the tertiary sector. In particular, the project pursues the following objectives:
1) reduce the waste coming from tertiary sector, that is characterized by short times for renewal of spaces and interiors. The project focuses especially on Lombardy territory, where a vast and various stock of tertiary buildings (offices, accommodation facilities, exhibition facilities, retail, temporary shops) is located. This stock of buildings is subject to frequent renewal interventions due to rapid obsolescence and temporary uses (e.g. temporary shops, exhibitions, design week, etc.).
2) maintain the economic value of building components coming from short-times renewals and to contain environmental impacts. The starting assumption is that the transformations within tertiary sector buildings are making available increasing quantities of materials and components, derived from dry assembled solutions, characterized by high added value and long-lasting useful life.
3) promote re-manufacturing and re-use (in overall terms “re-actions”, intended as: re-manufacturing, re-condition, re-purpose, re-use, and repair) as key strategies able to reduce the use of energy and materials compared to recycling.
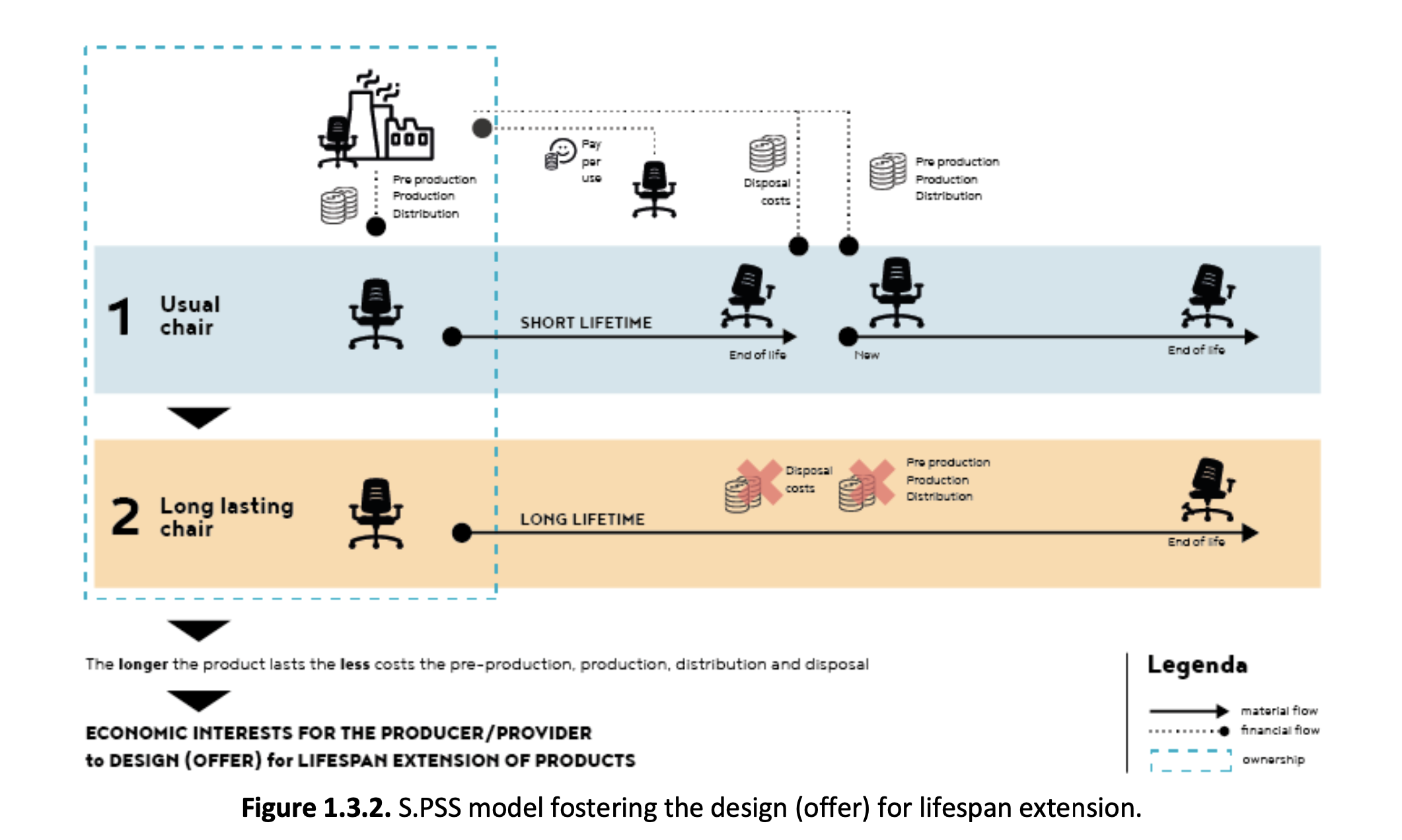
4) improve the competitiveness of various categories of stakeholders in Lombardy (e.g. small-medium manufacturing companies, FM services providers, etc.) by transferring in the construction sector new organizational and business models based on S.PSS (Sustainable Product-Service Systems), win-win strategies, and Life Cycle Management and by creating network relationships among operators.
5) define, and support through training, new jobs and professional skills in the field of re-manufacturing/re-use.
To this end, the project applies a multidisciplinary and multi-sectoral approach. The methodological approach of the whole research is characterized by cross-sectoral collaboration and cross-fertilization involving various disciplines and scientific areas (Technology of Architecture and Building construction, Management and Industrial Engineering, Industrial Design and Communication, Sustainable Design and Eco-design). The fields of skills and knowledge involved are related to: the building sector (operators, building process, building and construction technologies); the environmental and economic sustainability and Life Cycle Thinking; the business models and sharing economy; the eco-design and Sustainable Product-Service Systems. Many of the strategies and actions, related to these fields, are typically applied in other sectors: the research transfers and adapts them in the construction sector, defining organizational and operational models and rules, testing them through pilot stakeholder networks (including client/investors, manufacturers, facility managers, designers, installers, etc.) to assess their suitability.
Following this approach, the research proposes a framework of organizational and business models based on re-manufacturing and re-use of building components, encompassing:
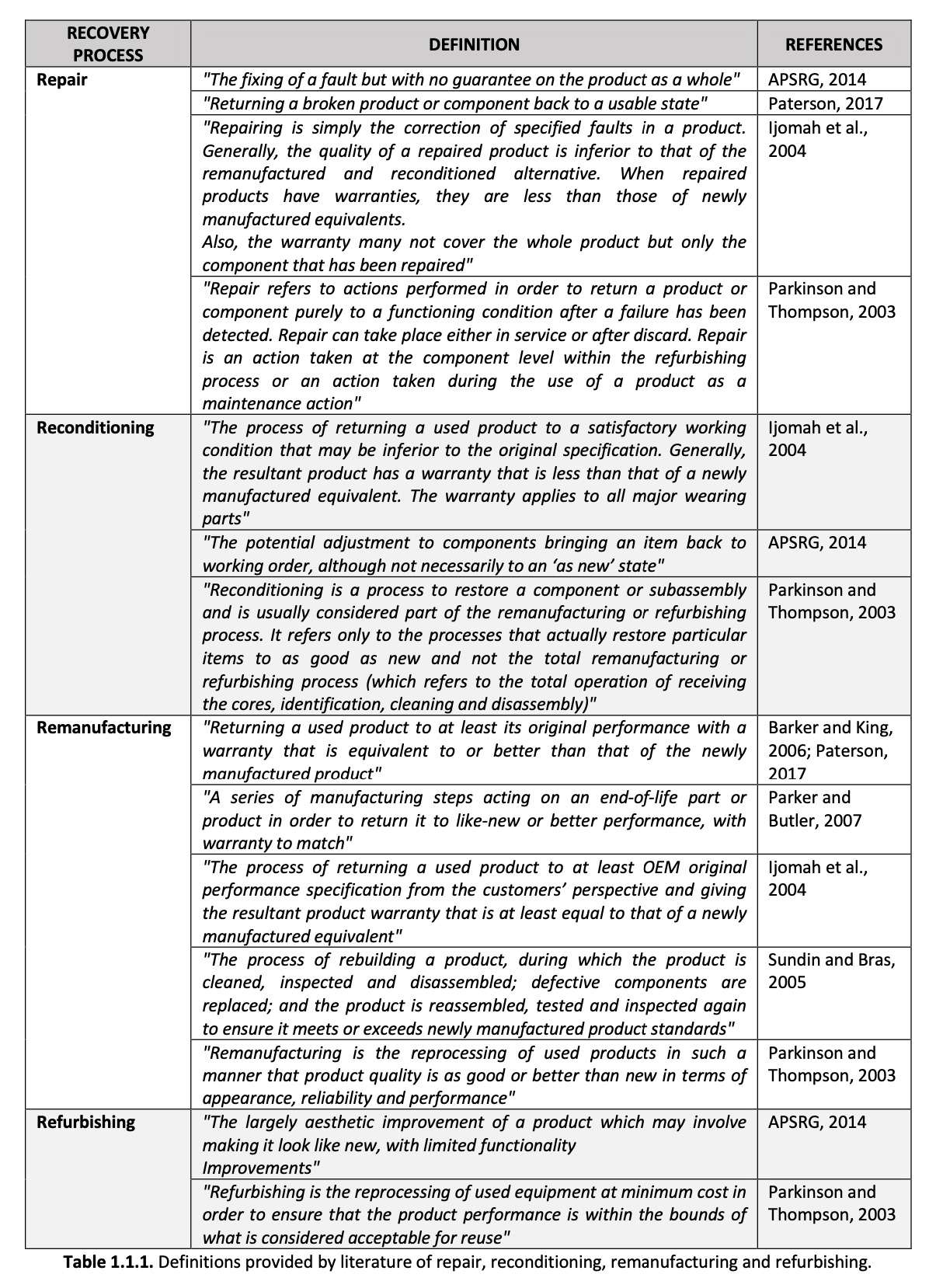
- definition of the features of the different re-actions, (re-manufacturing, re-condition, re-purpose, re-use, and repair) according to the specificity of the construction sector;
- definition of key criteria for re-manufacturing (design rules, identification keys): criteria for the design of components "to be re-manufactured"; interpretative keys to understand the re-manufacturing attitude of a component to be disassembled and re-manufactured; obstacles/barriers (e.g. legislative) and levers (e.g. guarantee conditions, certified environmental value, economic value);
- definition, through a multi-sectoral analysis, of: organizational conditions; criteria for the start of re- manufacturing processes; levers for the launch of successful re-manufacturing processes from an economic and environmental point of view; economic, environmental and social benefits to be used as levers for the start up of re-manufacturing processes;
- definition of rules to support the re-manufacturing processes: relationship rules (organizational, procedural, etc.); assembly, disassembly and processing procedures in relation to various technical elements (interior walls, finishes, floors, ceilings, external skin, windows frames); quality procedures, standards and methods for defining the characteristics of components easy to be re-manufactured; methods for exchanging materials and products; methods for sharing information and communication protocols; procedures of application of LC-based indicators aiming at identifying the environmentally and economically more effective strategies to be adopted in re-manufacturing processes (e.g. definition of the maximum advantageous physical distance between disassembly site and remanufacturer).
The framework of models based on re-manufacturing and re-use is tested through the development of pilot stakeholder network and two pilot projects.
In particular, the research is articulated into five Working Packages (WPs). In each WP, both Disciplinary Scientific Sectors collaborate, firstly adopting appropriate methods to each discipline, and secondarily fertilizing them in a continuous discussion between the different disciplinary approaches. The results of shared outputs will also be disseminated through publications and training courses / seminars.
EXTRACT WP1
Best practices of re-(use, manufacturing) and transferable key criteria to the construction sector
Introduction
Re-manufacturing and Re-use represent nowadays hot topics in various sectors - such as Aerospace, Automotive, Electronics, Machinery, Marine, Rail - that have already exploited its potential gaining multiple benefits in terms of environmental, social and economic sustainability. These practices are significantly growing in such sectors, gaining market share, creating new jobs and sharing experiences and knowledge by creating networks and associations (e.g. European Re-manufacturing Network, Conseil Européen de Remanufacture, ReuseIt Network - RIN, Re-manufacturing Industries Council - RIC, Centre for Re-manufacturing & Re-use - CRR, etc.). However, the construction sector is still not affected by these practices, although their application nowadays represents a shared priority at European level. Indeed, the European Commission identifies the construction sector as a ‘Priority area’ which has specific challenges in the context of circular economy: according to Eurostat, construction sector produces over a third of the total waste generated by all economic activities and households, it provides 18 million direct jobs and it contributes to about 9% of the EU’s GDP.
In this context, the report introduces the results of the research project "Re-NetTA (Re-manufacturing Networks for Tertiary Architectures). New organizational models and tools for re-manufacturing and re- using short life components coming from tertiary buildings renewal" developed at Politecnico di Milano and funded by Fondazione Cariplo. It aims to create the organizational and business conditions for activating regenerative circular processes in the field of transformation/redevelopment of buildings. In particular, it is focused on the tertiary sector, characterized by short-term cycles of renewals, with the purpose to extend the useful life of components and materials reducing the generation of waste.
The research work identifies a set of operative, organizational and business models in re-manufacturing practices, derived from other sectors, and verifies their transferability to the construction sector for a subsequent definition of replicable re-manufacturing models. To this end, a multidisciplinary and cross- sectoral methodological approach is implemented involving various disciplines and scientific areas, such as Technology of Architecture and Building construction, Management and Industrial Engineering, Industrial Design and Communication, Sustainable Design and Eco-design.
The findings of WP1 are, as first, the identification of the most suitable applications of “re-actions” (re- manufacturing, re-condition, repurpose, re-use, and repair) categories to the construction sector. Secondly, the definition of key criteria for re-manufacturing (e.g. design rules, identification keys), including criteria for the design for disassembly, as well as the main barriers (e.g. legislative) and levers (e.g. guarantee conditions, certified environmental value, economic value) for a future implementation. The results arisen during the research represent the first crucial step towards the activation of regenerative circular processes in the construction sector, contributing to maintain over time the value of the environmental and economic resources integrated into building components. WP2 will involve actions on the field and interviews with key operators, aiming at testing and validating the identified re- manufacturing models.
The present WP concerns the development of a framework of multi-disciplinary and multi-sectorial references useful for transfer purposes. The reference framework is developed according to the following tasks:
- Definition of the national and international State of Art of remanufacturing practices within industrial and construction sectors in a logic of a circular economy
- In-depth analysis of scientific works and funded research in order to identify best practices, approaches and trends in the field of circular processes aimed at reuse / remanufacturing.
- Investigation and identification of operative, organizational and business models in re-manufacturing practices of other sectors (e.g. automotive, electronics, etc.) that could be transferable to the construction sector.
- Survey and identification of cases of recurrent business models (e.g. SPSS, etc.) in other sectors (e.g. automotive, electronics, etc.) that could be transferable to the construction sector.
If you are interested in reading more send an email to remanufacturing-dabc@polimi.it or click on the button below and fill out the form
EXTRACT WP2
Field test and stakeholders’ identification
Shared method for business models development
In order to develop innovative and circular business models that can enable Re-manufacturing practices, the research followed a structured process that enhanced a strong multidisciplinary component.
Indeed, the methodological approach of the research (WP1 and WP2) is characterized by cross-sectoral collaboration and cross-fertilization starting from the skills and knowledge that characterize three DSS - Disciplinary Scientific Sectors (Technology of Architecture and Building construction - TAB, Management and Industrial Engineering - MIE, Industrial Design and Communication - IDC) and Sustainable Design and Eco-design - SDE).
Moreover, coherently with all the research activities in WP2, the process of business model development has been undertaken with a continuous relationship with stakeholders, involved from the early stages of the research through direct interviews.
The methodological steps implemented with the aim of defining plausible business models in the tertiary architecture sector can be summarized as follows:
1. Re-manufacturing literature and standard reference analysis. Analysis of literature and standard reference to reach a common definition of the term Re-manufacturing to take as a reference in the definition of the circular business models. In particular, in this research the term Re-manufacturing is intended as "re-action" (see Ch.1 of WP1 report), i.e. the system of activities which includes the following types of reworking of materials, components and products: disassembly, cleaning, replacement, repair, assembly and testing.
2. Cross-sector best practices analysis. Multiple best practices of business models based on Re-manufacturing occurring in different industrial sectors have been studied based on a common analysis framework with the aim to provide a comprehensive overview of real and comparable cases. In particular, the research analyzed the following sectors (see Ch. 3 of WP1 report): aerospace; automotive; electrical and electronic equipment; heavy-duty and off-road equipment; machinery; marine; transport; fashion; consumable and furniture sector.
3. Re-manufacturing best practices analysis in building industry. This sector has not yet been widely affected by circular reuse and Re-manufacturing practices. The most common practice is in fact the recycling of materials and products. However, some virtuous practices (see case studies in Ch. 6 of WP1 report) have been analyzed based on the shared case-studies framework, with the aim of understanding possible drivers and barriers related to the specificity of the construction sector, with particular reference to components for tertiary architectures.
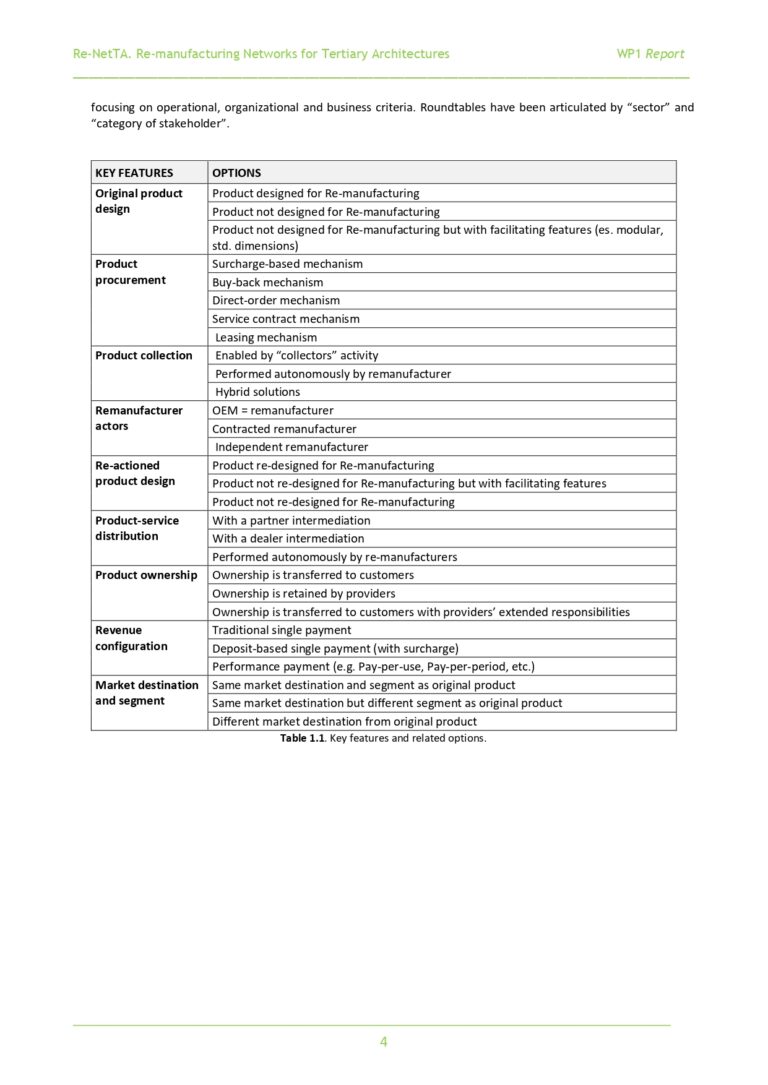
4. Definition of key features. Definition of a set of key features and related options able to describe the main characteristics of a business model in order to set up a common framework of description and representation of business models. In particular, the defined key features are: Original product design; Product procurement; Product collection; Remanufacturer actors; Re-actioned product design; Product-service distribution; Product ownership; Revenue configuration; Market destination and segment (see Ch.5 of WP1 report). For each key features, main options have been identified as shown in Table 1.1.
5. Recurring organizational model interpretation. Definition of recurring models, based on the abstraction from the specific case studies and on the subsequent generalization of relational and contractual models and material and monetary flows between the involved actors. This activity has been performed following a structured method based on the defined key features (point 4) able to describe the characteristics of the identified models.
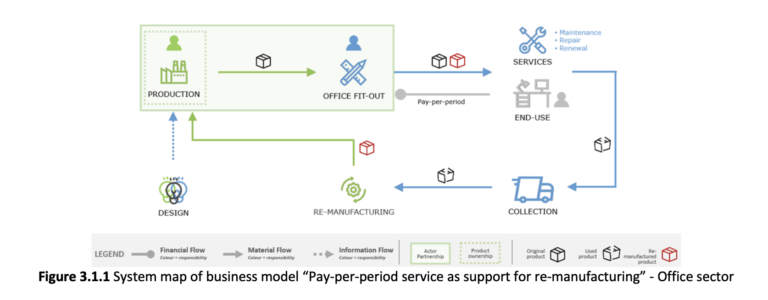
6. Tertiary architecture field study. Carrying out of an in-depth analysis of tertiary sub-sectors of application, e.g. exhibition sector, office sector, retail sector, etc. in order to characterize in detail the peculiarities of each sector to be able to adapt and adjust the generic models to the specific reference context relating to the sector being analyzed. The preliminary interviews with selected stakeholders – reported in chapter 3 - played a fundamental role in the characterization of the various sectors. They allowed to outline the identify needs, opportunities and obstacles to circular processes and businesses based on the re-manufacturing.
7. Proposal of organizational models. Definition and proposal of organizational models for the investigated sectors within the tertiary field (e.g. exhibition, retail, office, etc.) based on the interpretation of previous research activities and interview’s outcomes.
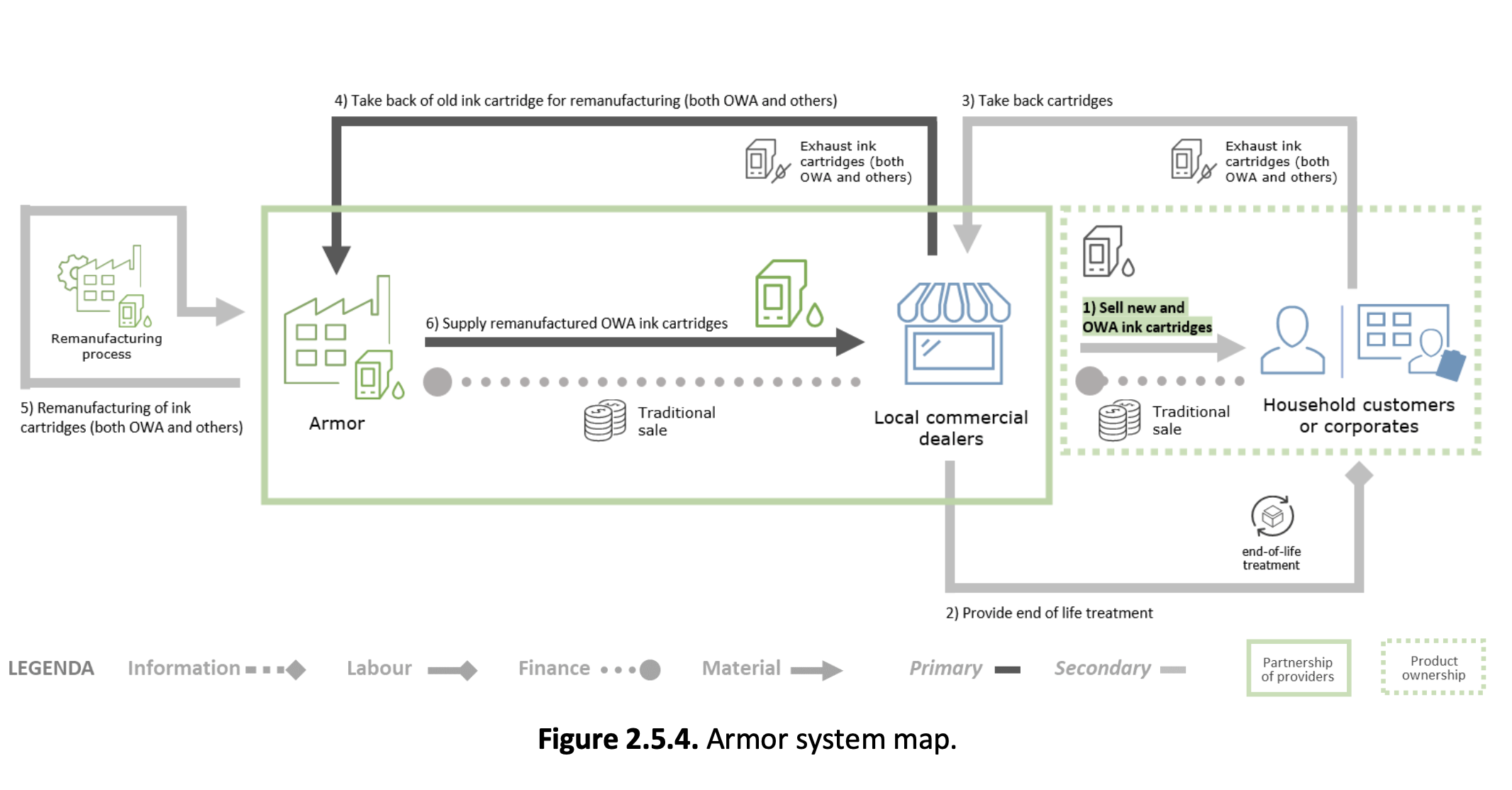
8. Organizational models validation. Verification of the applicability of the proposed business models, resulting from the multi-sectoral analysis of WP1 (cfr. WP2 paragraph 4.1, 4.2, 4.3). To achieve this aim, the investigation is based on the interaction among stakeholders. For this reason, a series of Roundtables has been set, in order to group medium-little groups of persons to enable the cooperative learning. Roundtables have been organized to promote debate between researchers and stakeholders through informal discussions. The Roundtable consists in two parts. In the first part, the Re-NetTA researchers propose a set of promising business models through the presentation of system maps. In the second part, questions and debates - concerning each proposed business models - take place, focusing on operational, organizational and business criteria. Roundtables have been articulated by “sector” and “category of stakeholder”.
If you are interested in reading more send an email to remanufacturing-dabc@polimi.it or click on the button below and fill out the form
EXTRACT WP3
Framework of models, rules and procedures for the remanufacturing of building components
Business models proposal
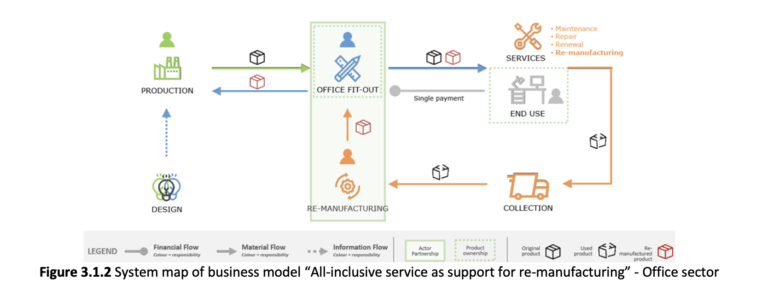
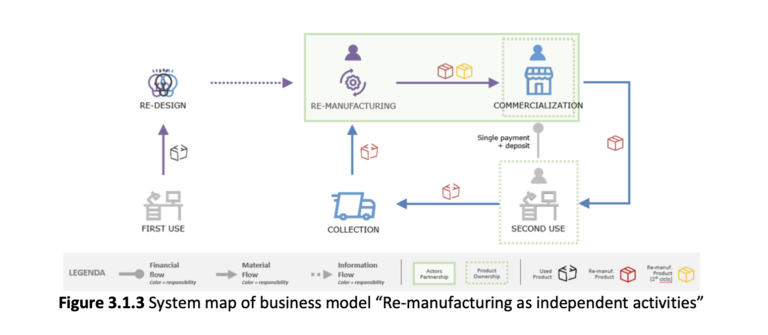
As evidenced by the previous WPs, the construction sector, unlike other industrial fields, is slow to experiment and apply sustainable re-manufacturing and reuse practices. Hence, WP3 intends to outline the conditions necessary to activate circular processes in the field of tertiary construction. In order to extend the life of construction products, three circular models based on re-manufacturing are presented, according to WP2 findings:
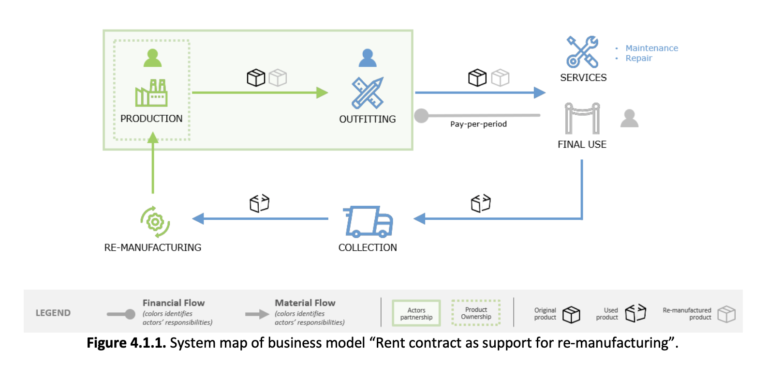
1. Rent contract as a support for re-manufacturing (BM1);
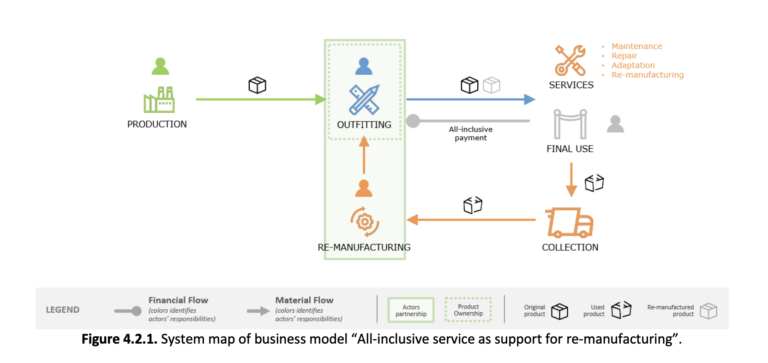
2. All-inclusive solution to support re-manufacturing (BM2);
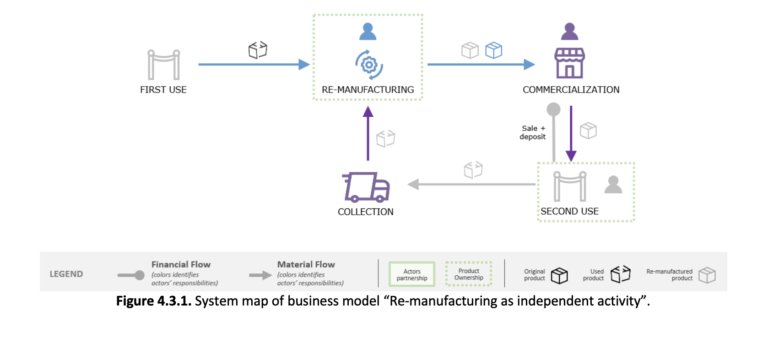
3. Product repurposing as a re-manufacturing strategy (BM3).
Developed with stakeholders and experts in an inter-sectoral and multidisciplinary approach, the proposed models represent a contribution towards sustainable design and organizational practices of construction products.
If you are interested in reading more send an email to remanufacturing-dabc@polimi.it or click on the button below and fill out the form
EXTRACT WP4
Pilot network for Remanufacturing and validation
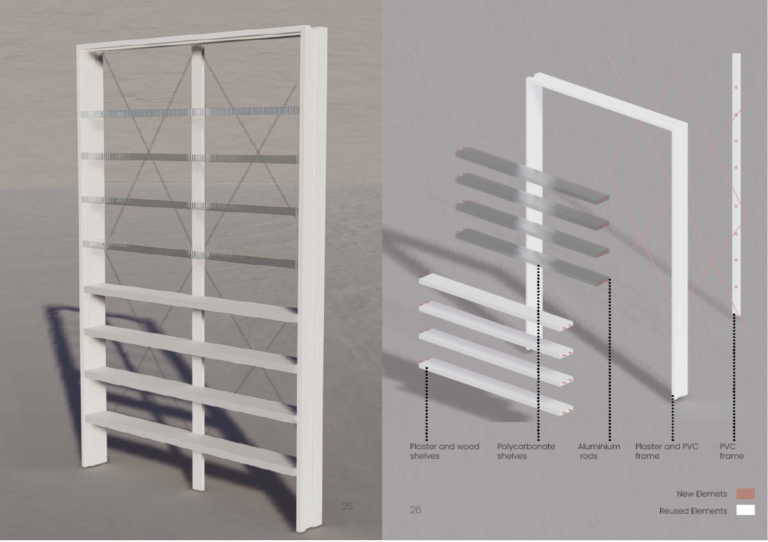
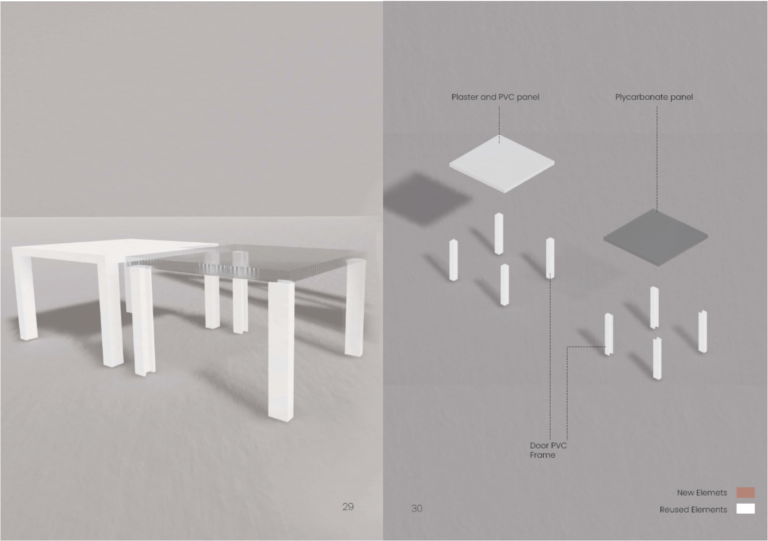
Pilot Project 01_ Investigation of remanufacturing design concepts for office doors
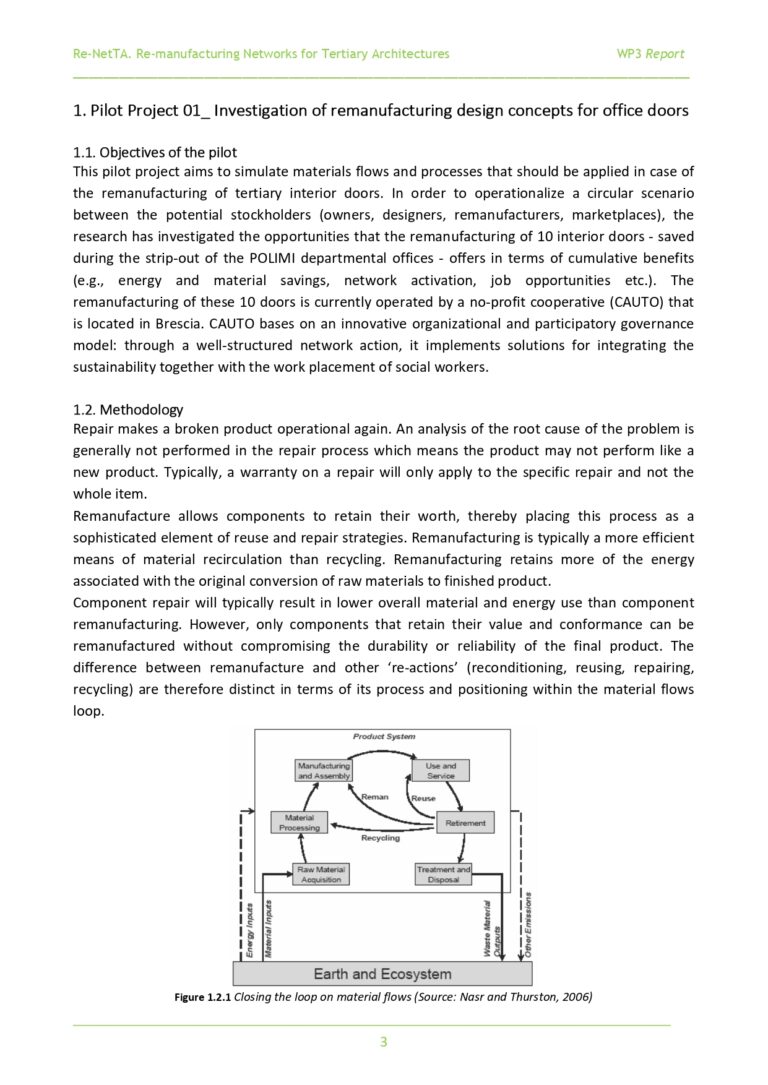
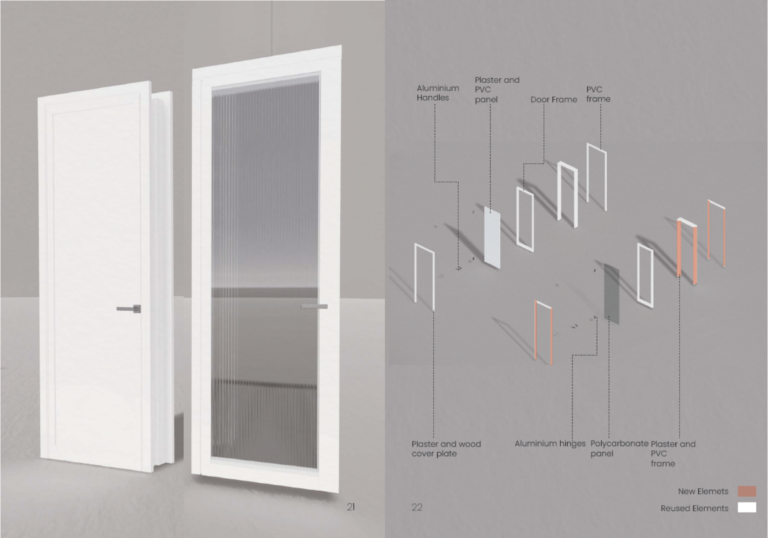
This pilot project aims to simulate materials flows and processes that should be applied in case of the remanufacturing of tertiary interior doors. In order to operationalize a circular scenario between the potential stockholders (owners, designers, remanufacturers, marketplaces), the research has investigated the opportunities that the remanufacturing of 10 interior doors - saved during the strip-out of the POLIMI departmental offices - offers in terms of cumulative benefits (e.g., energy and material savings, network activation, job opportunities etc.). The remanufacturing of these 10 doors is currently operated by a no-profit cooperative (CAUTO) that is located in Brescia. CAUTO bases on an innovative organizational and participatory governance model: through a well-structured network action, it implements solutions for integrating the sustainability together with the work placement of social workers.
If you are interested in reading more send an email to remanufacturing-dabc@polimi.it or click on the button below and fill out the form
Do you want to stay updated on the latest publications and dissemination activities?
Subscribe to the newsletter to stay updated on:
- Events, round tables and dissemination activities
- Latest publications and scientific articles
- Best practices and project activities
- Contact network